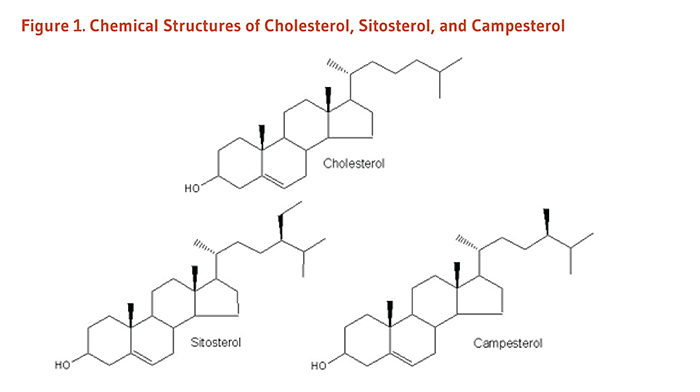
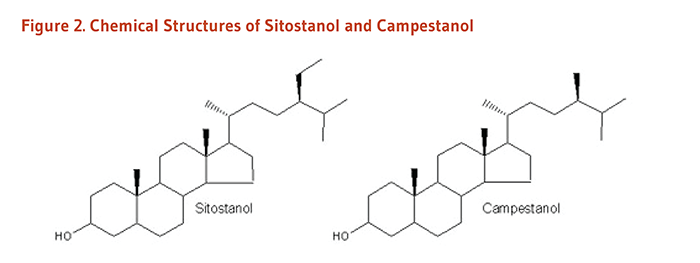
1. Jenkins DJ, Kendall CW, Marchie A, et al. The Garden of Eden--plant based diets, the genetic drive to conserve cholesterol and its implications for heart disease in the 21st century. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2003;136(1):141-151. (PubMed)
2. Kendall CW, Jenkins DJ. A dietary portfolio: maximal reduction of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol with diet. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2004;6(6):492-498. (PubMed)
3. Ostlund RE, Jr. Phytosterols in human nutrition. Annu Rev Nutr. 2002;22:533-549. (PubMed)
4. Sudhop T, Lutjohann D, von Bergmann K. Sterol transporters: targets of natural sterols and new lipid lowering drugs. Pharmacol Ther. 2005;105(3):333-341. (PubMed)
5. de Jong A, Plat J, Mensink RP. Metabolic effects of plant sterols and stanols (Review). J Nutr Biochem. 2003;14(7):362-369. (PubMed)
6. Plat J, Mensink RP. Plant stanol and sterol esters in the control of blood cholesterol levels: mechanism and safety aspects. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96(1 Suppl):15-22. (PubMed)
7. von Bergmann K, Sudhop T, Lutjohann D. Cholesterol and Plant Sterol Absorption: Recent Insights. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96(1S):10-14. (PubMed)
8. Ostlund RE, Jr., McGill JB, Zeng CM, et al. Gastrointestinal absorption and plasma kinetics of soy Delta(5)-phytosterols and phytostanols in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002;282(4):E911-916. (PubMed)
9. Sudhop T, Sahin Y, Lindenthal B, et al. Comparison of the hepatic clearances of campesterol, sitosterol, and cholesterol in healthy subjects suggests that efflux transporters controlling intestinal sterol absorption also regulate biliary secretion. Gut. 2002;51(6):860-863. (PubMed)
10. Berger A, Jones PJ, Abumweis SS. Plant sterols: factors affecting their efficacy and safety as functional food ingredients. Lipids Health Dis. 2004;3(1):5. (PubMed)
11. Katan MB, Grundy SM, Jones P, Law M, Miettinen T, Paoletti R. Efficacy and safety of plant stanols and sterols in the management of blood cholesterol levels. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003;78(8):965-978. (PubMed)
12. Nissinen M, Gylling H, Vuoristo M, Miettinen TA. Micellar distribution of cholesterol and phytosterols after duodenal plant stanol ester infusion. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002;282(6):G1009-1015. (PubMed)
13. Jones PJ, Raeini-Sarjaz M, Ntanios FY, Vanstone CA, Feng JY, Parsons WE. Modulation of plasma lipid levels and cholesterol kinetics by phytosterol versus phytostanol esters. J Lipid Res. 2000;41(5):697-705. (PubMed)
14. Normen L, Dutta P, Lia A, Andersson H. Soy sterol esters and beta-sitostanol ester as inhibitors of cholesterol absorption in human small bowel. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;71(4):908-913. (PubMed)
15. Richelle M, Enslen M, Hager C, et al. Both free and esterified plant sterols reduce cholesterol absorption and the bioavailability of beta-carotene and alpha-tocopherol in normocholesterolemic humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;80(1):171-177. (PubMed)
16. Plat J, Mensink RP. Effects of plant stanol esters on LDL receptor protein expression and on LDL receptor and HMG-CoA reductase mRNA expression in mononuclear blood cells of healthy men and women. FASEB J. 2002;16(2):258-260. (PubMed)
17. Mouritsen OG, Zuckermann MJ. What's so special about cholesterol? Lipids. 2004;39(11):1101-1113. (PubMed)
18. Halling KK, Slotte JP. Membrane properties of plant sterols in phospholipid bilayers as determined by differential scanning calorimetry, resonance energy transfer and detergent-induced solubilization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1664(2):161-171. (PubMed)
19. Awad AB, Chen YC, Fink CS, Hennessey T. beta-Sitosterol inhibits HT-29 human colon cancer cell growth and alters membrane lipids. Anticancer Res. 1996;16(5A):2797-2804. (PubMed)
20. Leikin AI, Brenner RR. Fatty acid desaturase activities are modulated by phytosterol incorporation in microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989;1005(2):187-191. (PubMed)
21. Ratnayake WM, L'Abbe MR, Mueller R, et al. Vegetable oils high in phytosterols make erythrocytes less deformable and shorten the life span of stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Nutr. 2000;130(5):1166-1178. (PubMed)
22. Ratnayake WM, Plouffe L, L'Abbe MR, Trick K, Mueller R, Hayward S. Comparative health effects of margarines fortified with plant sterols and stanols on a rat model for hemorrhagic stroke. Lipids. 2003;38(12):1237-1247. (PubMed)
23. Jones PJ, Raeini-Sarjaz M, Jenkins DJ, et al. Effects of a diet high in plant sterols, vegetable proteins, and viscous fibers (dietary portfolio) on circulating sterol levels and red cell fragility in hypercholesterolemic subjects. Lipids. 2005;40(2):169-174. (PubMed)
24. Awad AB, Hartati MS, Fink CS. Phytosterol feeding induces alteration in testosterone metabolism in rat tissues. J Nutr Biochem. 1998;9(12):712-717.
25. Cabeza M, Bratoeff E, Heuze I, Ramirez E, Sanchez M, Flores E. Effect of beta-sitosterol as inhibitor of 5 alpha-reductase in hamster prostate. Proc West Pharmacol Soc. 2003;46:153-155. (PubMed)
26. Hendriks HF, Brink EJ, Meijer GW, Princen HM, Ntanios FY. Safety of long-term consumption of plant sterol esters-enriched spread. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2003;57(5):681-692. (PubMed)
27. von Holtz RL, Fink CS, Awad AB. beta-Sitosterol activates the sphingomyelin cycle and induces apoptosis in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. Nutr Cancer. 1998;32(1):8-12. (PubMed)
28. Awad AB, Roy R, Fink CS. Beta-sitosterol, a plant sterol, induces apoptosis and activates key caspases in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2003;10(2):497-500. (PubMed)
29. Choi YH, Kong KR, Kim YA, et al. Induction of Bax and activation of caspases during beta-sitosterol-mediated apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2003;23(6):1657-1662. (PubMed)
30. Awad AB, Toczek J, Fink CS. Phytosterols decrease prostaglandin release in cultured P388D1/MAB macrophages. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2004;70(6):511-520. (PubMed)
31. Navarro A, De las Heras B, Villar A. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating properties of a sterol fraction from Sideritis foetens Clem. Biol Pharm Bull. 2001;24(5):470-473. (PubMed)
32. St-Onge MP, Jones PJ. Phytosterols and human lipid metabolism: efficacy, safety, and novel foods. Lipids. 2003;38(4):367-375. (PubMed)
33. Moruisi KG, Oosthuizen W, Opperman AM. Phytosterols/stanols lower cholesterol concentrations in familial hypercholesterolemic subjects: a systematic review with meta-analysis. J Am Coll Nutr. 2006;25(1):41-48. (PubMed)
34. Ellegard LH, Andersson SW, Normen AL, Andersson HA. Dietary plant sterols and cholesterol metabolism. Nutr Rev. 2007;65(1):39-45. (PubMed)
35. Van Horn L, McCoin M, Kris-Etherton PM, et al. The evidence for dietary prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease. J Am Diet Assoc. 2008;108(2):287-331. (PubMed)
36. Law M. Plant sterol and stanol margarines and health. BMJ. 2000;320(7238):861-864. (PubMed)
37. Chen JT, Wesley R, Shamburek RD, Pucino F, Csako G. Meta-analysis of natural therapies for hyperlipidemia: plant sterols and stanols versus policosanol. Pharmacotherapy. 2005;25(2):171-183. (PubMed)
38. AbuMweis SS, Barake R, Jones P. Plant sterols/stanols as cholesterol lowering agents: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Food & Nutrition Research. 2008; DOI: 10.3402/fnr.v52i0.1811. (PubMed)
39. Hendriks HF, Weststrate JA, van Vliet T, Meijer GW. Spreads enriched with three different levels of vegetable oil sterols and the degree of cholesterol lowering in normocholesterolaemic and mildly hypercholesterolaemic subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1999;53(4):319-327. (PubMed)
40. Miettinen TA, Vanhanen H. Dietary sitostanol related to absorption, synthesis and serum level of cholesterol in different apolipoprotein E phenotypes. Atherosclerosis. 1994;105(2):217-226. (PubMed)
41. Pelletier X, Belbraouet S, Mirabel D, et al. A diet moderately enriched in phytosterols lowers plasma cholesterol concentrations in normocholesterolemic humans. Ann Nutr Metab. 1995;39(5):291-295. (PubMed)
42. Sierksma A, Weststrate JA, Meijer GW. Spreads enriched with plant sterols, either esterified 4,4-dimethylsterols or free 4-desmethylsterols, and plasma total- and LDL-cholesterol concentrations. Br J Nutr. 1999;82(4):273-282. (PubMed)
43. Volpe R, Niittynen L, Korpela R, et al. Effects of yoghurt enriched with plant sterols on serum lipids in patients with moderate hypercholesterolaemia. Br J Nutr. 2001;86(2):233-239. (PubMed)
44. Hallikainen MA, Sarkkinen ES, Gylling H, Erkkila AT, Uusitupa MI. Comparison of the effects of plant sterol ester and plant stanol ester-enriched margarines in lowering serum cholesterol concentrations in hypercholesterolaemic subjects on a low-fat diet. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2000;54(9):715-725. (PubMed)
45. Vanstone CA, Raeini-Sarjaz M, Parsons WE, Jones PJ. Unesterified plant sterols and stanols lower LDL-cholesterol concentrations equivalently in hypercholesterolemic persons. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;76(6):1272-1278. (PubMed)
46. Weststrate JA, Meijer GW. Plant sterol-enriched margarines and reduction of plasma total- and LDL-cholesterol concentrations in normocholesterolaemic and mildly hypercholesterolaemic subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1998;52(5):334-343. (PubMed)
47. Miettinen TA, Puska P, Gylling H, Vanhanen H, Vartiainen E. Reduction of serum cholesterol with sitostanol-ester margarine in a mildly hypercholesterolemic population. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(20):1308-1312. (PubMed)
48. Wolfs M, de Jong N, Ocke MC, Verhagen H, Monique Verschuren WM. Effectiveness of customary use of phytosterol/-stanol enriched margarines on blood cholesterol lowering. Food Chem Toxicol. 2006;44(10):1682-1688. (PubMed)
49. Miettinen TA, Gylling H. Plant stanol and sterol esters in prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Ann Med. 2004;36(2):126-134. (PubMed)
50. O'Neill FH, Brynes A, Mandeno R, et al. Comparison of the effects of dietary plant sterol and stanol esters on lipid metabolism. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2004;14(3):133-142. (PubMed)
51. O'Neill FH, Sanders TA, Thompson GR. Comparison of efficacy of plant stanol ester and sterol ester: short-term and longer-term studies. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96(1A):29D-36D. (PubMed)
52. National Cholesterol Education Program. Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health. 2002. http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/cholesterol/atp3_rpt.htm.
53. Grundy SM. Stanol Esters as a Component of Maximal Dietary Therapy in the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III Report. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96(1 Suppl):47-50. (PubMed)
54. Jones PJ, Ntanios FY, Raeini-Sarjaz M, Vanstone CA. Cholesterol-lowering efficacy of a sitostanol-containing phytosterol mixture with a prudent diet in hyperlipidemic men. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999;69(6):1144-1150. (PubMed)
55. Jenkins DJ, Kendall CW, Marchie A, et al. Direct comparison of a dietary portfolio of cholesterol-lowering foods with a statin in hypercholesterolemic participants. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005;81(2):380-387. (PubMed)
56. Jenkins DJ, Kendall CW, Faulkner DA, et al. Assessment of the longer-term effects of a dietary portfolio of cholesterol-lowering foods in hypercholesterolemia. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;83(3):582-591. (PubMed)
57. Jenkins DJ, Kendall CW, Nguyen TH, et al. Effect of plant sterols in combination with other cholesterol-lowering foods. Metabolism. 2008;57(1):130-139. (PubMed)
58. Food and Drug Administration. Health claims: plant sterol/stanol esters and risk of coronary heart disease (CHD). US Government Printing Office. 2002. Available at: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/cfrsearch.cfm?fr=101.83. Accessed 3/3/15.
59. Ostlund RE, Jr. Phytosterols and cholesterol metabolism. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2004;15(1):37-41. (PubMed)
60. Ostlund RE, Jr., Racette SB, Stenson WF. Effects of trace components of dietary fat on cholesterol metabolism: phytosterols, oxysterols, and squalene. Nutr Rev. 2002;60(11):349-359. (PubMed)
61. Andersson SW, Skinner J, Ellegard L, et al. Intake of dietary plant sterols is inversely related to serum cholesterol concentration in men and women in the EPIC Norfolk population: a cross-sectional study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2004;58(10):1378-1385. (PubMed)
62. Klingberg S, Ellegard L, Johansson I, et al. Inverse relation between dietary intake of naturally occurring plant sterols and serum cholesterol in northern Sweden. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87(4):993-1001. (PubMed)
63. Ostlund RE, Jr., Racette SB, Okeke A, Stenson WF. Phytosterols that are naturally present in commercial corn oil significantly reduce cholesterol absorption in humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;75(6):1000-1004. (PubMed)
64. Ostlund RE, Jr., Racette SB, Stenson WF. Inhibition of cholesterol absorption by phytosterol-replete wheat germ compared with phytosterol-depleted wheat germ. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003;77(6):1385-1389. (PubMed)
65. Ju YH, Clausen LM, Allred KF, Almada AL, Helferich WG. beta-Sitosterol, beta-Sitosterol Glucoside, and a Mixture of beta-Sitosterol and beta-Sitosterol Glucoside Modulate the Growth of Estrogen-Responsive Breast Cancer Cells In Vitro and in Ovariectomized Athymic Mice. J Nutr. 2004;134(5):1145-1151. (PubMed)
66. Awad AB, Fink CS, Williams H, Kim U. In vitro and in vivo (SCID mice) effects of phytosterols on the growth and dissemination of human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2001;10(6):507-513. (PubMed)
67. Awad AB, Downie A, Fink CS, Kim U. Dietary phytosterol inhibits the growth and metastasis of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells grown in SCID mice. Anticancer Res. 2000;20(2A):821-824. (PubMed)
68. De Stefani E, Boffetta P, Ronco AL, et al. Plant sterols and risk of stomach cancer: a case-control study in Uruguay. Nutr Cancer. 2000;37(2):140-144. (PubMed)
69. Mendilaharsu M, De Stefani E, Deneo-Pellegrini H, Carzoglio J, Ronco A. Phytosterols and risk of lung cancer: a case-control study in Uruguay. Lung Cancer. 1998;21(1):37-45. (PubMed)
70. Ronco A, De Stefani E, Boffetta P, Deneo-Pellegrini H, Mendilaharsu M, Leborgne F. Vegetables, fruits, and related nutrients and risk of breast cancer: a case-control study in Uruguay. Nutr Cancer. 1999;35(2):111-119. (PubMed)
71. McCann SE, Freudenheim JL, Marshall JR, Brasure JR, Swanson MK, Graham S. Diet in the epidemiology of endometrial cancer in western New York (United States). Cancer Causes Control. 2000;11(10):965-974. (PubMed)
72. McCann SE, Freudenheim JL, Marshall JR, Graham S. Risk of human ovarian cancer is related to dietary intake of selected nutrients, phytochemicals and food groups. J Nutr. 2003;133(6):1937-1942. (PubMed)
73. Strom SS, Yamamura Y, Duphorne CM, et al. Phytoestrogen intake and prostate cancer: a case-control study using a new database. Nutr Cancer. 1999;33(1):20-25. (PubMed)
74. Berges RR, Windeler J, Trampisch HJ, Senge T. Randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial of beta-sitosterol in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Beta-sitosterol Study Group. Lancet. 1995;345(8964):1529-1532. (PubMed)
75. Berges RR, Kassen A, Senge T. Treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia with beta-sitosterol: an 18-month follow-up. BJU Int. 2000;85(7):842-846. (PubMed)
76. Klippel KF, Hiltl DM, Schipp B. A multicentric, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial of beta-sitosterol (phytosterol) for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. German BPH-Phyto Study group. Br J Urol. 1997;80(3):427-432. (PubMed)
77. Wilt TJ, MacDonald R, Ishani A. beta-sitosterol for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review. BJU Int. 1999;83(9):976-983. (PubMed)
78. Dreikorn K. The role of phytotherapy in treating lower urinary tract symptoms and benign prostatic hyperplasia. World J Urol. 2002;19(6):426-435. (PubMed)
79. Nair PP, Turjman N, Kessie G, et al. Diet, nutrition intake, and metabolism in populations at high and low risk for colon cancer. Dietary cholesterol, beta-sitosterol, and stigmasterol. Am J Clin Nutr. 1984;40(4 Suppl):927-930. (PubMed)
80. US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. USDA Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 20. 2007. Available at: http://www.nal.usda.gov/fnic/foodcomp/search/. Accessed 7/24/08.
81. Normen L, Bryngelsson S, Johnsson M, et al. The phytosterol content of some cereal foods commonly consumed in Sweden and in the Netherlands. J Food Compos Anal. 2002;15(6):693-704.
82. Normen L, Johnsson M, Andersson H, van Gameren Y, Dutta P. Plant sterols in vegetables and fruits commonly consumed in Sweden. Eur J Nutr. 1999;38(2):84-89. (PubMed)
83. Phillips KM, Ruggio DM, Toivo JI, Swank MA, Simpkins AH. Free and esterified sterol composition of edible oils and fats. J Food Compos Anal. 2002;15(2):123-142.
84. Mensink RP, Ebbing S, Lindhout M, Plat J, van Heugten MM. Effects of plant stanol esters supplied in low-fat yoghurt on serum lipids and lipoproteins, non-cholesterol sterols and fat soluble antioxidant concentrations. Atherosclerosis. 2002;160(1):205-213. (PubMed)
85. Plana N, Nicolle C, Ferre R, et al. Plant sterol-enriched fermented milk enhances the attainment of LDL-cholesterol goal in hypercholesterolemic subjects. Eur J Nutr. 2008;47(1):32-39. (PubMed)
86. Doornbos AM, Meynen EM, Duchateau GS, van der Knaap HC, Trautwein EA. Intake occasion affects the serum cholesterol lowering of a plant sterol-enriched single-dose yoghurt drink in mildly hypercholesterolaemic subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2006;60(3):325-333. (PubMed)
87. Noakes M, Clifton PM, Doornbos AME, Trautwein EA. Plant sterol ester-enriched milk and yoghurt effectively reduce serum cholesterol in modestly hypercholesterolemic subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2005;44(4):214-222. (PubMed)
88. Thomsen AB, Hansen HB, Christiansen C, Green H, Berger A. Effect of free plant sterols in low-fat milk on serum lipid profile in hypercholesterolemic subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2004;58(6):860-870. (PubMed)
89. Seppo L, Jauhiainen T, Nevala R, Poussa T, Korpela R. Plant stanol esters in low-fat milk products lower serum total and LDL cholesterol. Eur J Nutr. 2007;46(2):111-117. (PubMed)
90. Jauhiainen T, Salo P, Niittynen L, Poussa T, Korpela R. Effects of low-fat hard cheese enriched with plant stanol esters on serum lipids and apolipoprotein B in mildly hypercholesterolaemic subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2006;60(11):1253-1257. (PubMed)
91. Allen RR, Carson L, Kwik-Uribe C, Evans EM, Erdman JW, Jr. Daily consumption of a dark chocolate containing flavanols and added sterol esters affects cardiovascular risk factors in a normotensive population with elevated cholesterol. J Nutr. 2008;138(4):725-731. (PubMed)
92. Devaraj S, Jialal I, Vega-Lopez S. Plant sterol-fortified orange juice effectively lowers cholesterol levels in mildly hypercholesterolemic healthy individuals. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24(3):e25-28. (PubMed)
93. Devaraj S, Autret BC, Jialal I. Reduced-calorie orange juice beverage with plant sterols lowers C-reactive protein concentrations and improves the lipid profile in human volunteers. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;84(4):756-761. (PubMed)
94. Matvienko OA, Lewis DS, Swanson M, et al. A single daily dose of soybean phytosterols in ground beef decreases serum total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol in young, mildly hypercholesterolemic men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;76(1):57-64. (PubMed)
95. Plat J, van Onselen EN, van Heugten MM, Mensink RP. Effects on serum lipids, lipoproteins and fat soluble antioxidant concentrations of consumption frequency of margarines and shortenings enriched with plant stanol esters. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2000;54(9):671-677. (PubMed)
96. Food and Drug Administration. GRAS Notice No. GRN 000112. 2003. http://www.fda.gov/Food/IngredientsPackagingLabeling/GRAS/NoticeInventory/ucm153924.htm. Accessed 3/3/15.
97. Scientific Committee on Food. Opinion on Applications for Approval of a Variety of Plant Sterol-Enriched Foods. 2003. Available at: http://ec.europa.eu/food/fs/sc/scf/out174_en.pdf.
98. Ayesh R, Weststrate JA, Drewitt PN, Hepburn PA. Safety evaluation of phytosterol esters. Part 5. Faecal short-chain fatty acid and microflora content, faecal bacterial enzyme activity and serum female sex hormones in healthy normolipidaemic volunteers consuming a controlled diet either with or without a phytosterol ester-enriched margarine. Food Chem Toxicol. 1999;37(12):1127-1138. (PubMed)
99. Berge KE. Sitosterolemia: a gateway to new knowledge about cholesterol metabolism. Ann Med. 2003;35(7):502-511. (PubMed)
100. Stalenhoef AF, Hectors M, Demacker PN. Effect of plant sterol-enriched margarine on plasma lipids and sterols in subjects heterozygous for phytosterolaemia. J Intern Med. 2001;249(2):163-166. (PubMed)
101. Kwiterovich PO, Jr., Chen SC, Virgil DG, Schweitzer A, Arnold DR, Kratz LE. Response of obligate heterozygotes for phytosterolemia to a low-fat diet and to a plant sterol ester dietary challenge. J Lipid Res. 2003;44(6):1143-1155. (PubMed)
102. Normen L, Holmes D, Frohlich J. Plant sterols and their role in combined use with statins for lipid lowering. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2005;6(3):307-316. (PubMed)
103. Thompson GR. Additive effects of plant sterol and stanol esters to statin therapy. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96(1 Suppl):37-39. (PubMed)
104. Blair SN, Capuzzi DM, Gottlieb SO, Nguyen T, Morgan JM, Cater NB. Incremental reduction of serum total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol with the addition of plant stanol ester-containing spread to statin therapy. Am J Cardiol. 2000;86(1):46-52. (PubMed)
105. Neil HA, Meijer GW, Roe LS. Randomised controlled trial of use by hypercholesterolaemic patients of a vegetable oil sterol-enriched fat spread. Atherosclerosis. 2001;156(2):329-337. (PubMed)
106. Simons LA. Additive effect of plant sterol-ester margarine and cerivastatin in lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in primary hypercholesterolemia. Am J Cardiol. 2002;90(7):737-740. (PubMed)
107. Nguyen TT, Dale LC. Plant stanol esters and vitamin K. Mayo Clin Proc. 1999;74(6):642-643. (PubMed)
108. Raeini-Sarjaz M, Ntanios FY, Vanstone CA, Jones PJ. No changes in serum fat-soluble vitamin and carotenoid concentrations with the intake of plant sterol/stanol esters in the context of a controlled diet. Metabolism. 2002;51(5):652-656. (PubMed)
109. Korpela R, Tuomilehto J, Hogstrom P, et al. Safety aspects and cholesterol-lowering efficacy of low fat dairy products containing plant sterols. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2006;60(5):633-642. (PubMed)
110. Plat J, Mensink RP. Vegetable oil based versus wood based stanol ester mixtures: effects on serum lipids and hemostatic factors in non-hypercholesterolemic subjects. Atherosclerosis. 2000;148(1):101-112. (PubMed)
111. Plat J, Mensink RP. Effects of diets enriched with two different plant stanol ester mixtures on plasma ubiquinol-10 and fat-soluble antioxidant concentrations. Metabolism. 2001;50(5):520-529. (PubMed)
112. Ntanios FY, Duchateau GS. A healthy diet rich in carotenoids is effective in maintaining normal blood carotenoid levels during the daily use of plant sterol-enriched spreads. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2002;72(1):32-39. (PubMed)
113. Noakes M, Clifton P, Ntanios F, Shrapnel W, Record I, McInerney J. An increase in dietary carotenoids when consuming plant sterols or stanols is effective in maintaining plasma carotenoid concentrations. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;75(1):79-86. (PubMed)