1. Reed LJ. A trail of research from lipoic acid to alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(42):38329-38336. (PubMed)
2. Carreau JP. Biosynthesis of lipoic acid via unsaturated fatty acids. Methods Enzymol. 1979;62:152-158. (PubMed)
3. Smith AR, Shenvi SV, Widlansky M, Suh JH, Hagen TM. Lipoic acid as a potential therapy for chronic diseases associated with oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem. 2004;11(9):1135-1146. (PubMed)
4. Kramer K, Packer L. R-alpha-lipoic acid. In: Kramer K, Hoppe P, Packer L, eds. Nutraceuticals in Health and Disease Prevention. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc.; 2001:129-164.
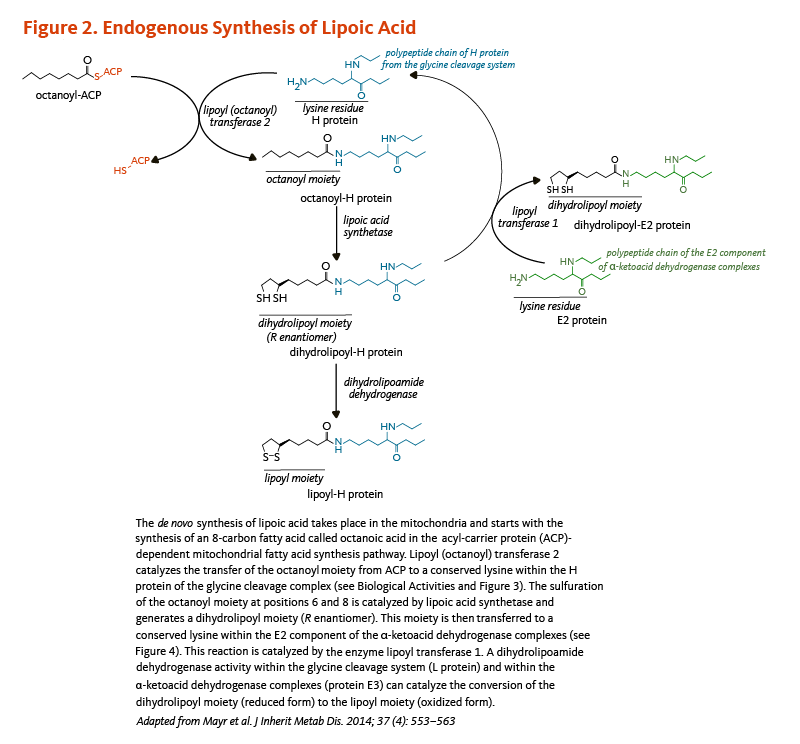
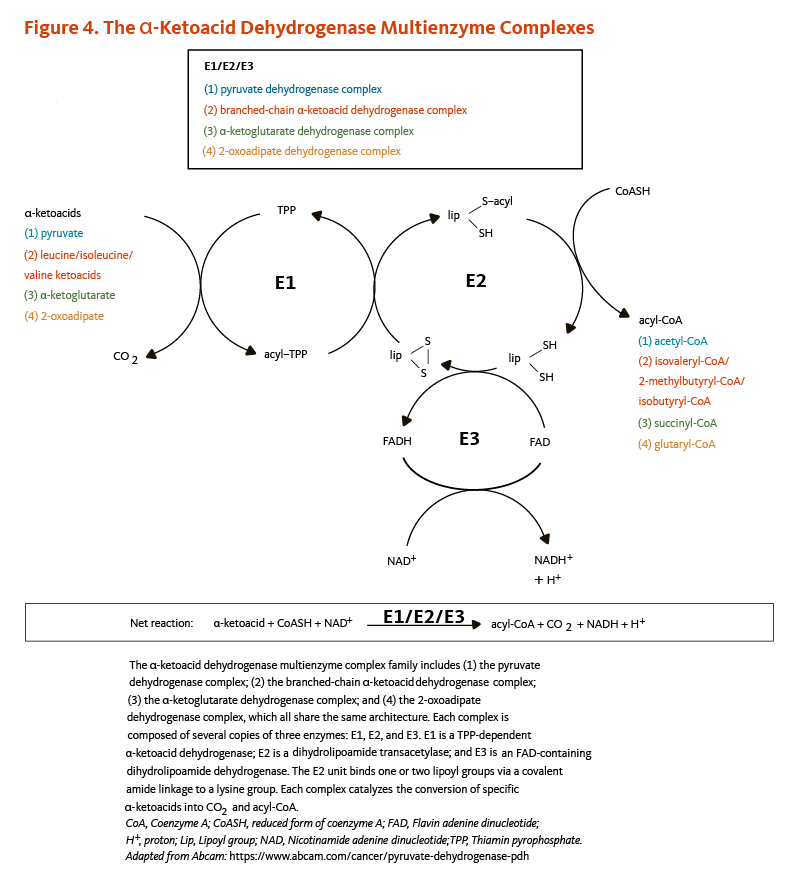
5. Mayr JA, Feichtinger RG, Tort F, Ribes A, Sperl W. Lipoic acid biosynthesis defects. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2014;37(4):553-563. (PubMed)
6. Hermann R, Niebch G, Borbe H, et al. Enantioselective pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of different racemic alpha-lipoic acid formulations in healthy volunteers. Eur J Pharm Sci. 1996;4(3):167-174.
7. Teichert J, Hermann R, Ruus P, Preiss R. Plasma kinetics, metabolism, and urinary excretion of alpha-lipoic acid following oral administration in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 2003;43(11):1257-1267. (PubMed)
8. Gleiter CH, Schug BS, Hermann R, Elze M, Blume HH, Gundert-Remy U. Influence of food intake on the bioavailability of thioctic acid enantiomers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1996;50(6):513-514. (PubMed)
9. Brufani M, Figliola R. (R)-alpha-lipoic acid oral liquid formulation: pharmacokinetic parameters and therapeutic efficacy. Acta Biomed. 2014;85(2):108-115. (PubMed)
10. Maglione E, Marrese C, Migliaro E, et al. Increasing bioavailability of (R)-alpha-lipoic acid to boost antioxidant activity in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Acta Biomed. 2015;86(3):226-233. (PubMed)
11. Breithaupt-Grogler K, Niebch G, Schneider E, et al. Dose-proportionality of oral thioctic acid--coincidence of assessments via pooled plasma and individual data. Eur J Pharm Sci. 1999;8(1):57-65. (PubMed)
12. Evans JL, Heymann CJ, Goldfine ID, Gavin LA. Pharmacokinetics, tolerability, and fructosamine-lowering effect of a novel, controlled-release formulation of alpha-lipoic acid. Endocr Pract. 2002;8(1):29-35. (PubMed)
13. Keith DJ, Butler JA, Bemer B, et al. Age and gender dependent bioavailability of R- and R,S-alpha-lipoic acid: a pilot study. Pharmacol Res. 2012;66(3):199-206. (PubMed)
14. Hiltunen JK, Autio KJ, Schonauer MS, Kursu VA, Dieckmann CL, Kastaniotis AJ. Mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis and respiration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1797(6-7):1195-1202. (PubMed)
15. Bustamante J, Lodge JK, Marcocci L, Tritschler HJ, Packer L, Rihn BH. Alpha-lipoic acid in liver metabolism and disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 1998;24(6):1023-1039. (PubMed)
16. Jones W, Li X, Qu ZC, Perriott L, Whitesell RR, May JM. Uptake, recycling, and antioxidant actions of alpha-lipoic acid in endothelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002;33(1):83-93. (PubMed)
17. Kozlov AV, Gille L, Staniek K, Nohl H. Dihydrolipoic acid maintains ubiquinone in the antioxidant active form by two-electron reduction of ubiquinone and one-electron reduction of ubisemiquinone. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1999;363(1):148-154. (PubMed)
18. May JM, Qu ZC, Mendiratta S. Protection and recycling of alpha-tocopherol in human erythrocytes by intracellular ascorbic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1998;349(2):281-289. (PubMed)
19. Upston JM, Terentis AC, Stocker R. Tocopherol-mediated peroxidation of lipoproteins: implications for vitamin E as a potential antiatherogenic supplement. Faseb J. 1999;13(9):977-994. (PubMed)
20. Valko M, Morris H, Cronin MT. Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem. 2005;12(10):1161-1208. (PubMed)
21. Doraiswamy PM, Finefrock AE. Metals in our minds: therapeutic implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2004;3(7):431-434. (PubMed)
22. Ou P, Tritschler HJ, Wolff SP. Thioctic (lipoic) acid: a therapeutic metal-chelating antioxidant? Biochem Pharmacol. 1995;50(1):123-126. (PubMed)
23. Suh JH, Zhu BZ, deSzoeke E, Frei B, Hagen TM. Dihydrolipoic acid lowers the redox activity of transition metal ions but does not remove them from the active site of enzymes. Redox Rep. 2004;9(1):57-61. (PubMed)
24. Suh JH, Moreau R, Heath SH, Hagen TM. Dietary supplementation with (R)-alpha-lipoic acid reverses the age-related accumulation of iron and depletion of antioxidants in the rat cerebral cortex. Redox Rep. 2005;10(1):52-60. (PubMed)
25. Yamamoto H, Watanabe T, Mizuno H, et al. The antioxidant effect of DL-alpha-lipoic acid on copper-induced acute hepatitis in Long-Evans Cinnamon (LEC) rats. Free Radic Res. 2001;34(1):69-80. (PubMed)
26. Patrick L. Mercury toxicity and antioxidants: Part 1: role of glutathione and alpha-lipoic acid in the treatment of mercury toxicity. Altern Med Rev. 2002;7(6):456-471. (PubMed)
27. Rooney JP. The role of thiols, dithiols, nutritional factors and interacting ligands in the toxicology of mercury. Toxicology. 2007;234(3):145-156. (PubMed)
28. Hagen TM, Vinarsky V, Wehr CM, Ames BN. (R)-alpha-lipoic acid reverses the age-associated increase in susceptibility of hepatocytes to tert-butylhydroperoxide both in vitro and in vivo. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2000;2(3):473-483. (PubMed)
29. Busse E, Zimmer G, Schopohl B, Kornhuber B. Influence of alpha-lipoic acid on intracellular glutathione in vitro and in vivo. Arzneimittelforschung. 1992;42(6):829-831. (PubMed)
30. Monette JS, Gomez LA, Moreau RF, et al. (R)-alpha-Lipoic acid treatment restores ceramide balance in aging rat cardiac mitochondria. Pharmacol Res. 2011;63(1):23-29. (PubMed)
31. Suh JH, Shenvi SV, Dixon BM, et al. Decline in transcriptional activity of Nrf2 causes age-related loss of glutathione synthesis, which is reversible with lipoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(10):3381-3386. (PubMed)
32. Suh JH, Wang H, Liu RM, Liu J, Hagen TM. (R)-alpha-lipoic acid reverses the age-related loss in GSH redox status in post-mitotic tissues: evidence for increased cysteine requirement for GSH synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2004;423(1):126-135. (PubMed)
33. Zhang J, Zhou X, Wu W, Wang J, Xie H, Wu Z. Regeneration of glutathione by alpha-lipoic acid via Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway alleviates cadmium-induced HepG2 cell toxicity. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2017;51:30-37. (PubMed)
34. Fratantonio D, Speciale A, Molonia MS, et al. Alpha-lipoic acid, but not di-hydrolipoic acid, activates Nrf2 response in primary human umbilical-vein endothelial cells and protects against TNF-alpha induced endothelium dysfunction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2018;655:18-25. (PubMed)
35. Sena CM, Cipriano MA, Botelho MF, Seica RM. Lipoic acid prevents high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis in Goto Kakizaki rats by reducing oxidative stress through Nrf2 activation. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(9). (PubMed)
36. Pilar Valdecantos M, Prieto-Hontoria PL, Pardo V, et al. Essential role of Nrf2 in the protective effect of lipoic acid against lipoapoptosis in hepatocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015;84:263-278. (PubMed)
37. Fayez AM, Zakaria S, Moustafa D. Alpha lipoic acid exerts antioxidant effect via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway activation and suppresses hepatic stellate cells activation induced by methotrexate in rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;105:428-433. (PubMed)
38. Lin YC, Lai YS, Chou TC. The protective effect of alpha-lipoic Acid in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury is mediated by heme oxygenase-1. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:590363. (PubMed)
39. Segal AW. The function of the NADPH oxidase of phagocytes and its relationship to other NOXs in plants, invertebrates, and mammals. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40(4):604-618. (PubMed)
40. Dong Y, Wang H, Chen Z. Alpha-lipoic acid attenuates cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via insulin receptor and PI3K/Akt-dependent inhibition of NADPH oxidase. Int J Endocrinol. 2015;2015:903186. (PubMed)
41. Byun E, Lim JW, Kim JM, Kim H. alpha-Lipoic acid inhibits Helicobacter pylori-induced oncogene expression and hyperproliferation by suppressing the activation of NADPH oxidase in gastric epithelial cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:380830. (PubMed)
42. Konrad D. Utilization of the insulin-signaling network in the metabolic actions of alpha-lipoic acid-reduction or oxidation? Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005;7(7-8):1032-1039. (PubMed)
43. Diesel B, Kulhanek-Heinze S, Holtje M, et al. Alpha-lipoic acid as a directly binding activator of the insulin receptor: protection from hepatocyte apoptosis. Biochemistry. 2007;46(8):2146-2155. (PubMed)
44. Estrada DE, Ewart HS, Tsakiridis T, et al. Stimulation of glucose uptake by the natural coenzyme alpha-lipoic acid/thioctic acid: participation of elements of the insulin signaling pathway. Diabetes. 1996;45(12):1798-1804. (PubMed)
45. Yaworsky K, Somwar R, Ramlal T, Tritschler HJ, Klip A. Engagement of the insulin-sensitive pathway in the stimulation of glucose transport by alpha-lipoic acid in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Diabetologia. 2000;43(3):294-303. (PubMed)
46. Ying Z, Kampfrath T, Sun Q, Parthasarathy S, Rajagopalan S. Evidence that alpha-lipoic acid inhibits NF-kappaB activation independent of its antioxidant function. Inflamm Res. 2011;60(3):219-225. (PubMed)
47. Smith AR, Hagen TM. Vascular endothelial dysfunction in aging: loss of Akt-dependent endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation and partial restoration by (R)-alpha-lipoic acid. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31(Pt 6):1447-1449. (PubMed)
48. Wang Y, Li X, Guo Y, Chan L, Guan X. alpha-Lipoic acid increases energy expenditure by enhancing adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase-peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1alpha signaling in the skeletal muscle of aged mice. Metabolism. 2010;59(7):967-976. (PubMed)
49. Moura FA, de Andrade KQ, dos Santos JC, Goulart MO. Lipoic acid: its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory role and clinical applications. Curr Top Med Chem. 2015;15(5):458-483. (PubMed)
50. Packer L, Cadenas E. Lipoic acid: energy metabolism and redox regulation of transcription and cell signaling. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2011;48(1):26-32. (PubMed)
51. Rochette L, Ghibu S, Richard C, Zeller M, Cottin Y, Vergely C. Direct and indirect antioxidant properties of alpha-lipoic acid and therapeutic potential. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013;57(1):114-125. (PubMed)
52. Shay KP, Moreau RF, Smith EJ, Smith AR, Hagen TM. Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1790(10):1149-1160. (PubMed)
53. Mayr JA, Zimmermann FA, Fauth C, et al. Lipoic acid synthetase deficiency causes neonatal-onset epilepsy, defective mitochondrial energy metabolism, and glycine elevation. Am J Hum Genet. 2011;89(6):792-797. (PubMed)
54. Tort F, Ferrer-Cortes X, Thio M, et al. Mutations in the lipoyltransferase LIPT1 gene cause a fatal disease associated with a specific lipoylation defect of the 2-ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(7):1907-1915. (PubMed)
55. Ziegler D. Thioctic acid for patients with symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy: a critical review. Treat Endocrinol. 2004;3(3):173-189. (PubMed)
56. Nathan DM, Davidson MB, DeFronzo RA, et al. Impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance: implications for care. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(3):753-759. (PubMed)
57. Jacob S, Henriksen EJ, Schiemann AL, et al. Enhancement of glucose disposal in patients with type 2 diabetes by alpha-lipoic acid. Arzneimittelforschung. 1995;45(8):872-874. (PubMed)
58. Jacob S, Rett K, Henriksen EJ, Haring HU. Thioctic acid--effects on insulin sensitivity and glucose-metabolism. Biofactors. 1999;10(2-3):169-174. (PubMed)
59. de Oliveira AM, Rondo PH, Luzia LA, D'Abronzo FH, Illison VK. The effects of lipoic acid and alpha-tocopherol supplementation on the lipid profile and insulin sensitivity of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;92(2):253-260. (PubMed)
60. Akbari M, Ostadmohammadi V, Lankarani KB, et al. The effects of alpha-lipoic acid supplementation on glucose control and lipid profiles among patients with metabolic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Metabolism. 2018;87:56-69. (PubMed)
61. Roberts AC, Porter KE. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction in diabetes. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2013;10(6):472-482. (PubMed)
62. Heitzer T, Finckh B, Albers S, Krohn K, Kohlschutter A, Meinertz T. Beneficial effects of alpha-lipoic acid and ascorbic acid on endothelium-dependent, nitric oxide-mediated vasodilation in diabetic patients: relation to parameters of oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 2001;31(1):53-61. (PubMed)
63. Heinisch BB, Francesconi M, Mittermayer F, et al. Alpha-lipoic acid improves vascular endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes: a placebo-controlled randomized trial. Eur J Clin Invest. 2010;40(2):148-154. (PubMed)
64. Xiang G, Pu J, Yue L, Hou J, Sun H. alpha-lipoic acid can improve endothelial dysfunction in subjects with impaired fasting glucose. Metabolism. 2011;60(4):480-485. (PubMed)
65. Xiang GD, Sun HL, Zhao LS, Hou J, Yue L, Xu L. The antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid improves endothelial dysfunction induced by acute hyperglycaemia during OGTT in impaired glucose tolerance. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2008;68(5):716-723. (PubMed)
66. Sola S, Mir MQ, Cheema FA, et al. Irbesartan and lipoic acid improve endothelial function and reduce markers of inflammation in the metabolic syndrome: results of the Irbesartan and Lipoic Acid in Endothelial Dysfunction (ISLAND) study. Circulation. 2005;111(3):343-348. (PubMed)
67. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Diabetic Neuropathy. Available at: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/preventing-problems/nerve-damage-diabetic-neuropathies. Accessed 9/23/18.
68. Malik RA, Tesfaye S, Ziegler D. Medical strategies to reduce amputation in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2013;30(8):893-900. (PubMed)
69. Obrosova IG. Diabetes and the peripheral nerve. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1792(10):931-940. (PubMed)
70. Dy SM, Bennett WL, Sharma R, et al. AHRQ Comparative Effectiveness Reviews. Preventing complications and treating symptoms of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2017. (PubMed)
71. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(14):977-986. (PubMed)
72. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998;352(9131):837-853. (PubMed)
73. Callaghan BC, Little AA, Feldman EL, Hughes RA. Enhanced glucose control for preventing and treating diabetic neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012(6):Cd007543. (PubMed)
74. Han T, Bai J, Liu W, Hu Y. A systematic review and meta-analysis of alpha-lipoic acid in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Eur J Endocrinol. 2012;167(4):465-471. (PubMed)
75. Ruhnau KJ, Meissner HP, Finn JR, et al. Effects of 3-week oral treatment with the antioxidant thioctic acid (alpha-lipoic acid) in symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabet Med. 1999;16(12):1040-1043. (PubMed)
76. Ziegler D, Hanefeld M, Ruhnau KJ, et al. Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid: a 7-month multicenter randomized controlled trial (ALADIN III Study). ALADIN III Study Group. Alpha-lipoic acid in diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care. 1999;22(8):1296-1301. (PubMed)
77. Ziegler D, Ametov A, Barinov A, et al. Oral treatment with alpha-lipoic acid improves symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy: the SYDNEY 2 trial. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(11):2365-2370. (PubMed)
78. Ziegler D, Low PA, Litchy WJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of antioxidant treatment with alpha-lipoic acid over 4 years in diabetic polyneuropathy: the NATHAN 1 trial. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(9):2054-2060. (PubMed)
79. Ziegler D, Low PA, Freeman R, Tritschler H, Vinik AI. Predictors of improvement and progression of diabetic polyneuropathy following treatment with alpha-lipoic acid for 4 years in the NATHAN 1 trial. J Diabetes Complications. 2016;30(2):350-356. (PubMed)
80. Balcioglu AS, Muderrisoglu H. Diabetes and cardiac autonomic neuropathy: Clinical manifestations, cardiovascular consequences, diagnosis and treatment. World J Diabetes. 2015;6(1):80-91. (PubMed)
81. Ziegler D, Schatz H, Conrad F, Gries FA, Ulrich H, Reichel G. Effects of treatment with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid on cardiac autonomic neuropathy in NIDDM patients. A 4-month randomized controlled multicenter trial (DEKAN Study). Deutsche Kardiale Autonome Neuropathie. Diabetes Care. 1997;20(3):369-373. (PubMed)
82. Nguyen N, Takemoto JK. A case for alpha-lipoic acid as an alternative treatment for diabetic polyneuropathy. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2018;21(1s):177s-191s. (PubMed)
83. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Diabetic Eye Disease. Available at: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/preventing-problems/diabetic-eye-disease. Accessed 9/24/18.
84. Gebka A, Serkies-Minuth E, Raczynska D. Effect of the administration of alpha-lipoic acid on contrast sensitivity in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:131538. (PubMed)
85. National Multiple Sclerosis Society. Definition of Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Available at: https://www.nationalmssociety.org/What-is-MS/Definition-of-MS. Accessed 9/28/18.
86. National Multiple Sclerosis Society. Types of Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Available at: https://www.nationalmssociety.org/What-is-MS/Types-of-MS. Accessed 9/28/18.
87. Marracci GH, Jones RE, McKeon GP, Bourdette DN. Alpha lipoic acid inhibits T cell migration into the spinal cord and suppresses and treats experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 2002;131(1-2):104-114. (PubMed)
88. Morini M, Roccatagliata L, Dell'Eva R, et al. Alpha-lipoic acid is effective in prevention and treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 2004;148(1-2):146-153. (PubMed)
89. Schreibelt G, Musters RJ, Reijerkerk A, et al. Lipoic acid affects cellular migration into the central nervous system and stabilizes blood-brain barrier integrity. J Immunol. 2006;177(4):2630-2637. (PubMed)
90. Salinthone S, Schillace RV, Marracci GH, Bourdette DN, Carr DW. Lipoic acid stimulates cAMP production via the EP2 and EP4 prostanoid receptors and inhibits IFN gamma synthesis and cellular cytotoxicity in NK cells. J Neuroimmunol. 2008;199(1-2):46-55. (PubMed)
91. Schillace RV, Pisenti N, Pattamanuch N, et al. Lipoic acid stimulates cAMP production in T lymphocytes and NK cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;354(1):259-264. (PubMed)
92. George JD, Kim E, Spain R, Bourdette D, Salinthone S. Effects of lipoic acid on migration of human B cells and monocyte-enriched peripheral blood mononuclear cells in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 2018;315:24-27. (PubMed)
93. Chaudhary P, Marracci GH, Bourdette DN. Lipoic acid inhibits expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 by CNS endothelial cells and T cell migration into the spinal cord in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 2006;175(1-2):87-96. (PubMed)
94. Marracci GH, McKeon GP, Marquardt WE, Winter RW, Riscoe MK, Bourdette DN. Alpha lipoic acid inhibits human T-cell migration: implications for multiple sclerosis. J Neurosci Res. 2004;78(3):362-370. (PubMed)
95. Yadav V, Marracci G, Lovera J, et al. Lipoic acid in multiple sclerosis: a pilot study. Mult Scler. 2005;11(2):159-165. (PubMed)
96. Yadav V, Marracci GH, Munar MY, et al. Pharmacokinetic study of lipoic acid in multiple sclerosis: comparing mice and human pharmacokinetic parameters. Mult Scler. 2010;16(4):387-397. (PubMed)
97. Khalili M, Eghtesadi S, Mirshafiey A, et al. Effect of lipoic acid consumption on oxidative stress among multiple sclerosis patients: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Nutr Neurosci. 2014;17(1):16-20. (PubMed)
98. Khalili M, Azimi A, Izadi V, et al. Does lipoic acid consumption affect the cytokine profile in multiple sclerosis patients: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2014;21(6):291-296. (PubMed)
99. Khalili M, Soltani M, Moghadam SA, Dehghan P, Azimi A, Abbaszadeh O. Effect of alpha-lipoic acid on asymmetric dimethylarginine and disability in multiple sclerosis patients: A randomized clinical trial. Electron Physician. 2017;9(7):4899-4905. (PubMed)
100. Molz P, Schroder N. Potential therapeutic effects of lipoic acid on memory deficits related to aging and neurodegeneration. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:849. (PubMed)
101. Hager K, Marahrens A, Kenklies M, Riederer P, Munch G. Alpha-lipoic acid as a new treatment option for Azheimer type dementia. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2001;32(3):275-282. (PubMed)
102. Hager K, Kenklies M, McAfoose J, Engel J, Munch G. Alpha-lipoic acid as a new treatment option for Alzheimer's disease--a 48 months follow-up analysis. J Neural Transm Suppl. 2007(72):189-193. (PubMed)
103. Dana Consortium on the Therapy of HIV Dementia and Related Cognitive Disorders. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of deprenyl and thioctic acid in human immunodeficiency virus-associated cognitive impairment. Neurology. 1998;50(3):645-651. (PubMed)
104. Shinto L, Quinn J, Montine T, et al. A randomized placebo-controlled pilot trial of omega-3 fatty acids and alpha lipoic acid in Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;38(1):111-120. (PubMed)
105. Namazi N, Larijani B, Azadbakht L. Alpha-lipoic acid supplement in obesity treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Clin Nutr. 2018;37(2):419-428. (PubMed)
106. Kucukgoncu S, Zhou E, Lucas KB, Tek C. Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) as a supplementation for weight loss: results from a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev. 2017;18(5):594-601. (PubMed)
107. Lodge JK, Youn HD, Handelman GJ, et al. Natural sources of lipic acid: determination of lipoyllysine released from protease-digested tissues by high performance liquid chromatography incorporating electrochemical detection. J Appl Nutr. 1997;49(1 & 2):3-11.
108. Biewenga GP, Haenen GR, Bast A. The pharmacology of the antioxidant lipoic acid. Gen Pharmacol. 1997;29(3):315-331. (PubMed)
109. ConsumerLab.com. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Supplements Review July 2017. Available at: https://www.consumerlab.com/reviews/Alpha-Lipoic_Acid_Supplements/alphalipoic/. Accessed 9/27/18.
110. Streeper RS, Henriksen EJ, Jacob S, Hokama JY, Fogt DL, Tritschler HJ. Differential effects of lipoic acid stereoisomers on glucose metabolism in insulin-resistant skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1997;273(1 Pt 1):E185-191. (PubMed)
111. Maitra I, Serbinova E, Tritschler HJ, Packer L. Stereospecific effects of R-lipoic acid on buthionine sulfoximine-induced cataract formation in newborn rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;221(2):422-429. (PubMed)
112. Ziegler D, Nowak H, Kempler P, Vargha P, Low PA. Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid: a meta-analysis. Diabet Med. 2004;21(2):114-121. (PubMed)
113. Reljanovic M, Reichel G, Rett K, et al. Treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant thioctic acid (alpha-lipoic acid): a two year multicenter randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial (ALADIN II). Alpha Lipoic Acid in Diabetic Neuropathy. Free Radic Res. 1999;31(3):171-179. (PubMed)
114. Parente E, Colannino G, Picconi O, Monastra G. Safety of oral alpha-lipoic acid treatment in pregnant women: a retrospective observational study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(18):4219-4227. (PubMed)
115. Natural Medicines. Alpha-Lipoic Acid/Safety - Professional Handout. Available at: https://naturalmedicines.therapeuticresearch.com. Accessed 9/26/18.
116. Karaarslan U, Isguder R, Bag O, Kisla M, Agin H, Unal N. Alpha lipoic acid intoxication, treatment and outcome. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2013;51(6):522. (PubMed)
117. Hadzik B, Grass H, Mayatepek E, Daldrup T, Hoehn T. Fatal non-accidental alpha-lipoic acid intoxication in an adolescent girl. Klin Padiatr. 2014;226(5):292-294. (PubMed)
118. Natural Medicines. Alpha-Lipoic acid/Interactions with Drugs - Professional handout. Available at: https://naturalmedicines.therapeuticresearch.com. Accessed 9/25/18.
119. Gleiter CH, Schreeb KH, Freudenthaler S, et al. Lack of interaction between thioctic acid, glibenclamide and acarbose. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1999;48(6):819-825. (PubMed)
120. Prasad PD, Wang H, Huang W, et al. Molecular and functional characterization of the intestinal Na+-dependent multivitamin transporter. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1999;366(1):95-106. (PubMed)
121. Balamurugan K, Vaziri ND, Said HM. Biotin uptake by human proximal tubular epithelial cells: cellular and molecular aspects. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005;288(4):F823-831. (PubMed)
122. Zempleni J, Trusty TA, Mock DM. Lipoic acid reduces the activities of biotin-dependent carboxylases in rat liver. J Nutr. 1997;127(9):1776-1781. (PubMed)
123. Zempleni J, Mock DM. Biotin biochemistry and human requirements. J Nutr Biochem. 1999;10(3):128-138. (PubMed)